Merry Christmas
From our family to yours, Merry Christmas.
And remember — Santa comes down the chimney, not through your inbox. That “urgent gift card” email isn’t from the North Pole.

Why IoT Devices Are a Hidden Security Risk for Your Business
…and how to protect your network before it’s too late

We all love the convenience of connected devices. Smart thermostats, IP security cameras, Wi-Fi printers they’re everywhere in today’s small business and home-office setups. But with that convenience comes risk. So, what risk is posed by internet of things devices?
Many Internet of Things (IoT) devices are built for speed-to-market, not security. And when they’re connected to your business network, they can become a back door for attackers.
Here’s what you need to know and how ExchangeDefender can help keep your systems safe.
The Attack Surface Just Got Bigger
Every IoT device is basically another computer on your network often with weaker defenses. From smart sensors to printers to cameras, they connect and they communicate.
A recent report found that nearly half of all network connections involving IoT devices originate from high-risk equipment (unpatched, misconfigured, or insecure).
(Source: TechRadar)
If you leave devices unmonitored or on the same network as your PCs and servers, you’re handing attackers a faster route to your data.
Built-In Weaknesses (That Attackers Love)
Here are the most common IoT failings:
- Weak/default passwords — Many devices ship with generic admin logins. (Keyfactor)
- No encryption or insecure protocols — Some devices transmit data in plain text. (EMnify)
- Unpatched firmware — Devices often stop receiving updates, leaving vulnerabilities open. (OVIC)
- Unsegmented networks — Mixing IoT with critical systems is a recipe for risk. (Fortinet)
In short: IoT devices often lack enterprise-grade security controls, making them easy entry points for hackers.
The Real-World Risks
Here’s how things can go wrong fast:
- A compromised security camera becomes part of a botnet launching attacks. (Wikipedia: Mirai Malware)
- A smart building sensor with default credentials is used to access internal systems.
- An unpatched industrial IoT device introduces ransomware into a manufacturing network.
- IoT devices leak sensitive data after vendors stop issuing updates.
If you’re a small or medium-sized business (SMB), you’re both agile and vulnerable. IoT devices often fall into the “too small to worry about” category until they become the problem.
What matters most is visibility, segmentation, and defense.
How ExchangeDefender Helps
Protecting your network doesn’t mean hunting down every smart bulb it means building layers.
- Email & threat filtering: Even if attackers get in, phishing is their next move. We block that.
- Network segmentation support: Isolate IoT traffic and protect core systems.
- Policy control & visibility: Know what’s connected and manage permissions.
- Compliance coverage: IoT vulnerabilities can lead to compliance failures: we help plug that gap.
Simple Steps You Can Take Today
- Audit: Make a list of every connected device: printers, sensors, cameras, etc.
- Segment: Create a separate network for IoT traffic.
- Update: Keep firmware current. Replace devices no longer supported.
- Secure Credentials: Change default passwords and enable MFA.
- Monitor Traffic: Watch for odd connection patterns.
- Vet Vendors: Work only with IoT vendors that offer security transparency and updates.
IoT is now part of every modern business but if you ignore it, you invite risk. By segmenting, auditing, and protecting connected devices, you can enjoy innovation and security.
ExchangeDefender helps you build a layered defense, so even the smallest device on your network doesn’t become your biggest security hole.
ExchangeDefender Rolls Out Advanced ‘Reject Policies’ for Safer Inboxes

At ExchangeDefender we’ve always seen ourselves as the firewall that keeps unwanted email content entering or exiting our clients network. To keep compliance simple we never deleted emails – if the content was objectionable we would scan it, log it, and let org and user policies choose what happens to the message.
As the email world becomes more dangerous, with AI capable of conducting social engineering scams at scale, IT teams are looking for new policies that can handle it.
At ExchangeDefender we work closely with our partners around the world and this feature is courtesy of Tommy from Twisted Networx.

Tommy is hardly alone when it comes to this issue, some businesses pride themselves on the amount of money they spend on aggressive marketing via email. Ghost resubscribes, unsubscribe pages not working, confusing UI to trick you into buying or sharing info, and endless scams are just a part of business on the Internet these days. It’s something ExchangeDefender can help you fix.
We’re introducing Reject Policies.
If you’ve identified an organization you do not want to communicate with for any reason, or if you have a network you want to keep out, or if you just want a quieter quarantine: ExchangeDefender will now reject the email on your behalf and you will never have to see it again.
For compliance purposes we will of course log the rejection in the Domain Admin logging facility at https://admin.exchangedefender.com but the message meta and any data will be rejected at the edge of the ExchangeDefender network. This way you will still be able to troubleshoot mail flow and make adjustments as needed.
We’re building a more flexible, powerful ExchangeDefender to meet real-world business challenges—and your feedback plays a big part in that. If you’ve got ideas that could make your email experience more secure or productive, we’d love to hear them.
New features and updated policies are rolling out later this fall. Stay in the loop by visiting https://support.exchangedefender.com, checking out our blog, or following us on social media.
How to Protect Sensitive Data in Your Emails

Because “Oops” isn’t a great security plan.
Let’s be honest—email is kind of the backbone of your business. It’s where deals get made, contracts are sent, invoices fly back and forth, and sometimes, if we’re being real, it’s where you accidentally email your lunch order to the entire company.
But here’s the thing: your inbox is also a treasure trove of sensitive information. We’re talking payment details, client data, logins, internal documents—the kind of stuff cybercriminals dream about at night.
And yet, most of us treat email like it’s just another casual chat box.
So, what’s the risk?
Imagine sending a postcard with your bank account number written on it. That’s kind of what emailing sensitive info without protection is like. Most email travels unencrypted, which means anyone snooping along the way can read it. That includes hackers, scammers, and even that one weird guy on public Wi-Fi at the coffee shop.
Phishing scams are getting slicker, malware is getting smarter, and businesses—especially small ones—are being targeted more than ever. The result? Breaches, downtime, lost money, and a lot of “We probably should’ve encrypted that” conversations.
But protecting your email doesn’t have to be hard.
Seriously. You don’t need a cybersecurity degree or a 20-person IT department. You just need the right tool—and that’s where ExchangeDefender Email Encryption comes in.
It’s designed to make secure emailing feel… well, normal. No hoops, no complicated setup. Just a simple way to keep your messages private, even if they’re packed with sensitive info.
With ExchangeDefender, you can send encrypted messages right from your browser, protect them with a password if you want, and even set expiration dates—so your email isn’t just floating around forever. You also get full visibility: when your message is opened, by who, and where. (Which makes you look really smart during audits, by the way.)
Plus, it plays nice with compliance rules like HIPAA and GDPR, which is a big win if you’re in healthcare, finance, or just… trying not to get fined.

Here’s the bottom line:
If you’re using email to run your business, you need to protect what’s inside. Email encryption is one of the easiest, most impactful things you can do—and ExchangeDefender makes it painless.
So next time you’re about to hit “send” on something important, ask yourself:
What would it cost me if this fell into the wrong hands?
Then go encrypt it. We’ll help.
Why Email Security Isn’t Optional Anymore (Even for Small Businesses)

Once upon a time, email security was something only big corporations worried about—firewalls, encryption, threat detection… it all sounded like enterprise stuff.
But those days? Long gone.
If your business has an email address (and let’s be honest, who doesn’t?), you’re already a target. And the bad guys? They’re counting on you thinking security is “someone else’s problem.”
Let’s break down why email security is no longer optional—especially for small businesses.
1. Small Businesses Are Easy Targets
Cybercriminals know that smaller companies don’t always have the time, money, or resources to invest in advanced security tools. That’s exactly why they get hit more often.
Think of it this way: would a burglar go after Fort Knox… or the house with the front door wide open?
2. Phishing Scams Are Smarter (and Meaner)
Today’s phishing emails don’t look like Nigerian prince spam. They’re clean. Branded. Personalized.
They might come from what looks like your vendor, your CEO, or even your bank.
They want you to click the link, download the invoice, or reset your password.
And they’re sneaky good at it.
That’s why real-time threat detection and phishing filters are essential—not just “nice to have.”
3. Email Holds the Keys to Your Business
Think about it: your inbox is a treasure chest of…
- Client communications
- Invoices and payment links
- Internal documents
- Credentials and logins
- Contracts, quotes, and private notes
If someone gains access to your email, they don’t just read your messages—they own your business operations. And the recovery costs (both financially and reputation-wise) are brutal.

4. The Cost of NOT Securing Email Is Way Higher
Sure, tools like ExchangeDefender cost money. But do you know what costs more?
- Downtime
- Breach cleanup
- Legal fees
- Lost client trust
Email security is no longer a cost center—it’s a business continuity solution.
5. The Right Tools Make Security Simple
You don’t need to hire a team of security experts. ExchangeDefender helps small businesses stay protected with:
✅ Spam + phishing filters
✅ Email encryption
✅ Real-time malware scanning
✅ Quarantine reports + trusted sender controls
✅ Simulated phishing training
✅ 24/7 monitoring + support
It’s not just about defense—it’s about peace of mind.
Your email is your front door. Lock it.
Small business or not, today’s threats are real—and relentless. But with the right protection in place, you can focus on growing your business instead of chasing down security fires.
🔐 Want to see how ExchangeDefender can keep your email secure? Let’s talk.
The Anatomy of a Phishing Email (With Examples)

Phishing emails have come a long way from the hilariously obvious scams of the early 2000s. Today, they’re more convincing, better designed, and — worst of all — more effective. Knowing how to spot a phishing email can mean the difference between avoiding a breach… or becoming the next cautionary tale.
Let’s break down the anatomy of a phishing email — using real examples and highlighting the red flags you should never ignore.
What is Phishing?
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack where cybercriminals pose as trusted entities to trick people into giving up sensitive information — like passwords, credit card numbers, or access credentials. These emails may look like they’re from your boss, your bank, or even your favorite app.
Key Elements to Watch For
Let’s dissect a classic phishing email and highlight where the danger hides:
1. Weird or Slightly Off Email Address

Example: ceo@exchanqedefender.com instead of ceo@exchangedefender.com
A single letter can be all it takes to trick someone. Always double-check the sender’s email. If it looks “off,” it probably is.
👉 Pro Tip: Hover over the sender’s email or tap to reveal full details.
2. Urgent or Threatening Language

Example: “Your account has been suspended due to suspicious activity. Click below to restore access.”
Scammers want you to act fast without thinking. Anything that demands “immediate action” is likely designed to panic you into clicking.
3. Generic Greetings

Example: “Dear user” or “Hi customer”
If it’s a real company emailing you, they probably know your name. Phishing emails often use vague intros to cast a wide net.
4. Suspicious Links or Attachments

Example: A button that says “Restore Account” but links to a random URL like http://secure-login-info.com
Always hover before you click. If the URL doesn’t match the legitimate site, run far away (and don’t open attachments either).
5. Spelling + Grammar Errors

Even today, many phishing emails are riddled with typos and weird formatting.
Example: “You acount has been suspened. Click hear to restore”
You’d be surprised how many people overlook this — don’t be one of them.
✅ How to Protect Yourself
- Slow down. Urgency is a tactic.
- Verify. If in doubt, call or message the sender directly (don’t reply).
- Train your team. Run phishing simulations regularly.
- Use protection. Email filtering tools like ExchangeDefender can stop threats before they hit your inbox.
Phishing emails rely on one thing: human error. But with awareness, training, and the right tools, you can turn your team into a human firewall. Learn what to look for — and don’t let the phish hook you.
Want to test your team’s phishing detection skills?
👉 Try our free phishing simulation today
Stay safe. Stay alert. Stay unphished.
How the eBay Phishing Scam Works

The eBay phishing scam is a common cyberattack where scammers impersonate eBay to steal user credentials, financial details, or personal information. These scams often take the form of fake emails, text messages, or websites designed to trick users into providing sensitive information.
In eBay phishing scams, attackers send counterfeit emails or messages that appear to originate from eBay. These communications often contain urgent prompts, such as warnings about account issues or unauthorized transactions, compelling recipients to click on malicious links. These links lead to fake websites resembling eBay’s login page, where users are tricked into entering their credentials. Once obtained, cybercriminals can exploit this information for fraudulent activities, including unauthorized purchases or identity theft.

Red Flags to Watch Out For:
🚨 Generic Greetings – Legitimate eBay emails usually address you by name. Look for fake logos!
🚨 Suspicious Links – Hover over links before clicking—real eBay links should start with “ebay.com.”
🚨 Poor Grammar & Spelling – Many phishing emails have obvious errors. Look for fake phone numbers!
🚨 Requests for Personal Info – eBay never asks for passwords, payment info, or security details via email.
How to Protect Yourself:
✅ Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) for extra security.
✅ Go Directly to eBay – Instead of clicking links, log in at eBay.com.
✅ Report Suspicious Emails to eBay at spoof@ebay.com.
✅ Use Strong, Unique Passwords – Avoid reusing your eBay password on other sites.
Mitigating Phishing Risks with ExchangeDefender PRO
To safeguard against such evolving threats, businesses require robust cybersecurity solutions. ExchangeDefender PRO offers comprehensive email security designed to protect organizations from advanced email-borne attacks. Key features include:
Anti-Phishing Protection: Identifies and blocks phishing attempts, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Anti-Spam and Malware Defense: Filters out spam and detects malicious attachments, reducing the risk of malware infections.
Ransomware Protection: Guards against ransomware attacks that can encrypt critical business data.
Domain Fraud Prevention: Prevents spoofing and unauthorized use of your domain, protecting your brand’s integrity.
On-Demand Encryption: Ensures sensitive communications are securely encrypted, maintaining confidentiality.
Adding ExchangeDefender PRO to your cybersecurity setup can help protect your organization from phishing scams and other email threats. It’s a smart way to stay safe online and keep your business and relationships secure.
How to Spot & Avoid the Latest DocuSign Scam

Cybercriminals are getting craftier, and one of their favorite new tricks is impersonating trusted services like DocuSign. If you’ve recently received an email urging you to sign a document or verify your account, think twice before clicking! The latest wave of DocuSign email scams is designed to steal your personal information and compromise your security.
How the DocuSign Email Scam Works
Scammers send fake emails that appear to be from DocuSign, using official-looking branding and urgent messaging. Here’s how the scam typically unfolds:
- Fake Email Notification – You receive an email that looks like it’s from DocuSign, requesting you to review or sign a document.
- Urgency & Pressure – The email often claims the document requires your immediate attention, creating a sense of urgency.
- Malicious Links – Clicking the link redirects you to a fraudulent website that mimics DocuSign’s login page.
- Credential Theft – If you enter your login details, scammers steal them to access your DocuSign or other linked accounts.
- Malware Installation – Some scams include attachments or links that, when clicked, install malware on your device.

Red Flags to Watch For
These scams can be convincing, but there are a few telltale signs that can help you identify them:
✔ Suspicious Sender Address – Official DocuSign emails come from @docusign.com or @docusign.net, not random or misspelled domains.
✔ Unusual Language or Errors – Many phishing emails contain typos, grammatical mistakes, or odd phrasing. Look for fake logos as well!
✔ Unexpected Requests – If you weren’t expecting a document, verify with the sender before opening anything.
✔ Fake Links – Hover over any links in the email (without clicking) to see the actual URL. If it’s not docusign.com, don’t trust it.
✔ Generic Greetings – Scammers often use “Dear Customer” instead of your actual name.
How to Stay Safe
Protect yourself and your business from falling victim to these scams by following these best practices:
🔹 Verify Directly – Instead of clicking email links, go to www.docusign.com and log in to check if a document is waiting.
🔹 Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – Adding an extra layer of security can prevent unauthorized access to your account.
🔹 Report Suspicious Emails – If you receive a fraudulent DocuSign email, forward it to spam@docusign.com and then delete it.
🔹 Keep Security Software Updated – Use up-to-date antivirus and security software to detect and block phishing attempts.
🔹 Educate Your Team – Ensure employees know how to recognize and avoid phishing emails.
Is That PayPal Email Real? How to Spot a Phishing Scam

PayPal is a convenient way to send and receive money online, but it’s also a popular target for scammers. PayPal phishing scams aim to trick you into handing over your login details or other sensitive information, potentially leading to financial loss and identity theft. At ExchangeDefender, we’re committed to helping you stay safe online, so let’s break down how these scams work and, more importantly, how to avoid them.
How PayPal Phishing Works
Imagine receiving an email that looks exactly like it’s from PayPal. It uses the familiar logo, branding, and even sounds official. The message might say there’s been unauthorized activity on your account, that your account has been limited, or that you need to update your information. It creates a sense of urgency, urging you to act quickly.
This is the core of a phishing scam. The email contains a link that leads to a fake website designed to mimic the real PayPal login page. If you enter your username and password on this fake site, the scammers instantly capture your information and can use it to access your real PayPal account.

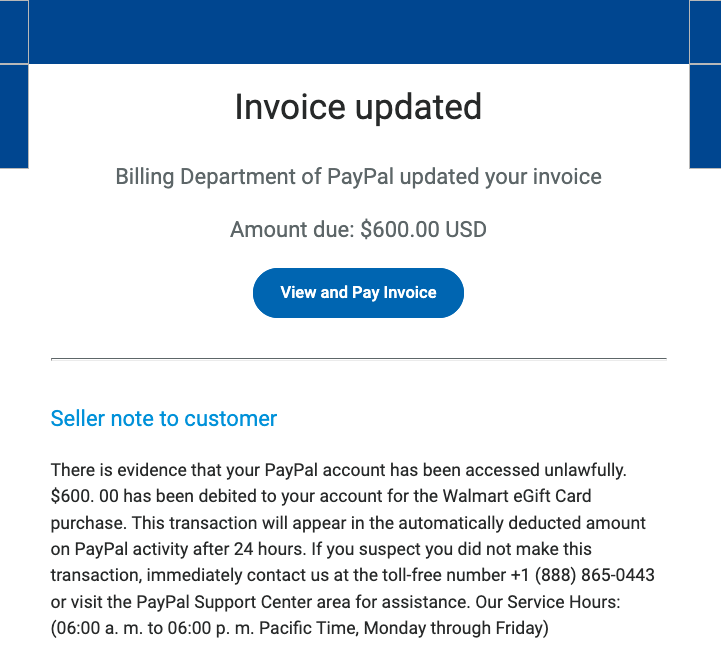
Common Red Flags to Watch Out For:
- Unexpected Emails or Messages: Be suspicious of any unsolicited communication claiming to be from PayPal. Legitimate companies rarely ask for sensitive information via email or text.
- Urgent or Threatening Language: Scammers often use language that creates a sense of panic, such as “Your account will be suspended” or “Immediate action required.”
- Suspicious Links: Hover your mouse over any link without clicking to see the actual URL. Look for misspellings, unusual characters, or domains that don’t match PayPal’s official website (www.paypal.com).
- Generic Greetings: Phishing emails often use generic greetings like “Dear Customer” instead of your name.
- Requests for Personal Information: PayPal will never ask for your password, bank account details, or credit card numbers directly in an email.
Protecting Yourself: Practical Tips
Here are some simple but effective steps you can take to protect yourself from PayPal phishing scams:
- Never Click Links in Suspicious Emails: Always go directly to the PayPal website by typing www.paypal.com into your browser’s address bar. This ensures you’re on the legitimate site.
- Check the Sender’s Email Address: Carefully examine the sender’s email address. Look for any misspellings or unusual characters. Legitimate PayPal emails usually come from addresses ending in @paypal.com.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): 2FA adds an extra layer of security to your account by requiring a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your phone.
- Be Wary of Attachments: Avoid opening attachments from suspicious emails, as they may contain malware.
- Report Suspicious Activity: If you receive a suspicious email or message, forward it to phishing@paypal.com.
ExchangeDefender: Your Partner in Cybersecurity
At ExchangeDefender, we’re dedicated to providing comprehensive cybersecurity solutions to protect you from online threats. While we can’t prevent every phishing email from reaching your inbox, we can empower you with the knowledge and tools to identify and avoid them. By staying vigilant and following these tips, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to a PayPal phishing scam.
The Latest Cyber Threats You Need to Know About (2025 Edition)

The cyber threat landscape is constantly evolving, with new and sophisticated attacks emerging every day. In 2025, we’re seeing a convergence of several concerning trends:
1. AI-Powered Attacks:
- Sophisticated Phishing: AI is now generating incredibly convincing phishing emails, making them harder to detect.
- Automated Exploits: AI can quickly identify and exploit vulnerabilities in systems, launching attacks at unprecedented speeds.
- Deepfakes: AI-generated deepfakes are becoming increasingly realistic, making it difficult to distinguish between real and fabricated content, leading to social engineering and disinformation campaigns.
2. The Rise of IoT Attacks:
- With the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in homes and businesses, attack surfaces are expanding dramatically.
- Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities in connected devices to gain access to sensitive information or even control critical infrastructure.
3. Cloud Security Challenges:
- As more businesses migrate to the cloud, the security of cloud environments becomes increasingly critical.
- Cloud misconfigurations, vulnerabilities in cloud services, and insider threats pose significant challenges.
4. Ransomware 2.0:
- Ransomware attacks are becoming more sophisticated and targeted, with attackers demanding higher ransoms and threatening to release sensitive data publicly.
To stay safe online, practice strong password hygiene, be wary of suspicious emails and links, keep your devices and software updated, and be mindful of what you share online. The cyber threat landscape is constantly evolving, but by staying informed and taking proactive steps to protect yourself, you can minimize your risk of falling victim to cyberattacks.









